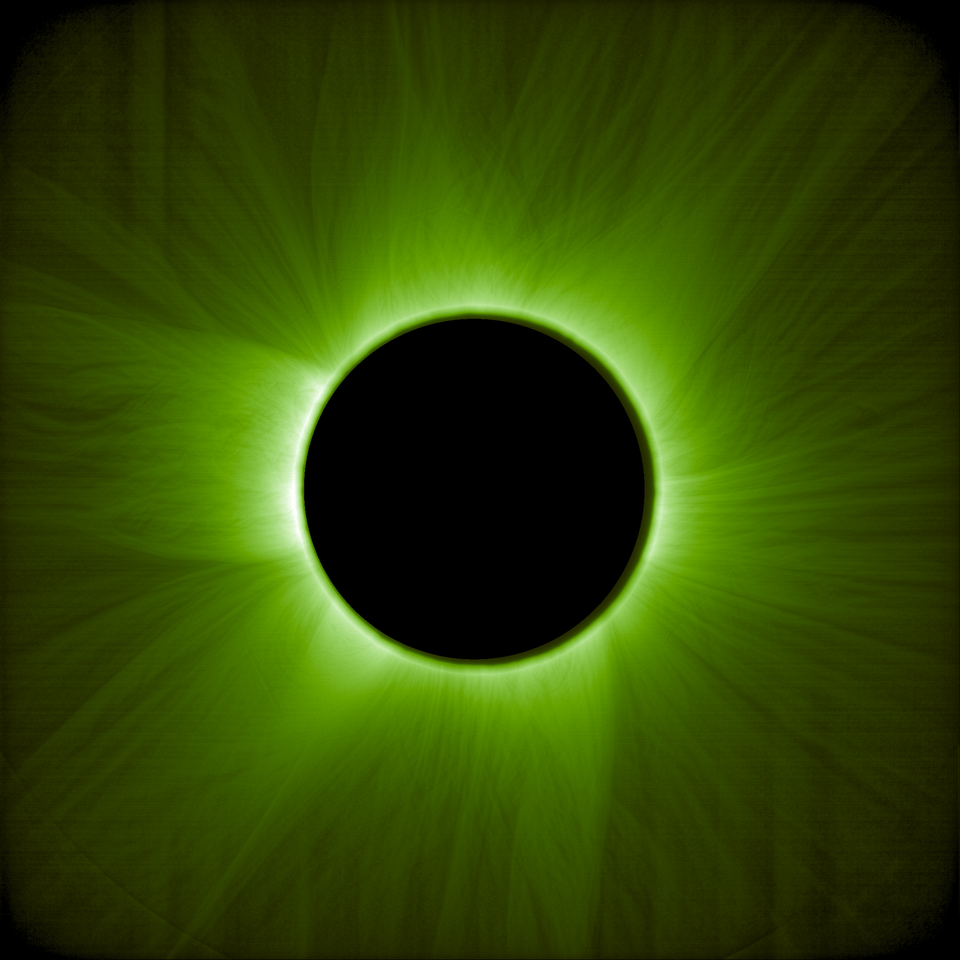
Proba-3 shows first images of solar corona thanks to autonomous formation flying
The Proba-3 space mission shows the first images of the solar corona as a result of the high-precision formation flying and is making progress in achieving its scientific and technological objectives.
In recent weeks, GMV personnel have been on hand at ESEC, the mission's operations center, providing on-site support to the teams at the European Space Agency (ESA) and Sener as part of the component commissioning activities that have enabled the autonomous formation flight of the two spacecraft making up the mission and the acquisition of the first images of the solar corona presented recently.
Proba-3 is a mission being led by Spain, with Sener coordinating a consortium of 40 companies from 16 countries. It is based on two satellites: the Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC) and the Occulter Spacecraft (OSC), which will be flying at a distance of 150 meters apart. The mission’s main objective is to demonstrate the feasibility of advanced formation flight technologies. This enables the creation of a virtual solid structure in space, functioning as a single instrument designed to make detailed observations of the solar corona. The OSC blocks the Sun’s light by generating an artificial eclipse, which will make it possible for the CSC to observe the solar corona without interference.
In the context of this innovative mission, GMV is responsible for the formation flying subsystem (FFS), which is considered to be the Proba‑3 project’s most advanced, complex, and critical component. The purpose of this FFS is to allow the two satellites to maintain the precision and stability necessary to operate as a single virtual rigid structure, which will require millimeter precision in positioning and arcsecond precision in orientation. Through its subsidiary in Poland, GMV is also playing a key role in designing and validating the onboard function for calculating relative positioning based on GPS measurements integrated into the FFS. GMV has also developed the ground system responsible for flight dynamics verification (Flight Dynamics System, or FDS). This system is responsible for orbit determination, event prediction and maneuver calculation, making sure that the satellites maintain formation throughout the mission, and it will provide support to operations during the initial, most critical phases.
As a result of the activities carried out over the last few weeks, the two vehicles have achieved formation flight with millimeter precision, enabling images of the solar corona to be obtained by generating an artificial eclipse of the OSC over the CSC instrument responsible for obtaining the images of the solar corona.
The images presented validate the high-precision formation flight and its application for the study of the solar corona through the creation of an artificial eclipse controlled with unprecedented precision.